3D printer manufacturer Stratasys has published its second environmental, social and governance and sustainability (ESG) report.
Completed in accordance with the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standards, the document highlights the environmental sustainability and social impact of the company’s additive manufacturing technology.
Within its inaugural sustainability report, published in 2022, Stratasys announced a commitment to achieving more ‘mindful manufacturing’ through 3D printing, particularly with regard to renewable energy.
Now, the firm believes that it is delivering on these commitments, with its technology actively enabling manufacturers to transition to more sustainable practices. To support this, the new report highlights several environmental, social and governance-based achievements.
Notably, the company claims to have reduced 207 metric tons of CO2 emission through the adoption of renewable energy at its facilities, as well as reducing 3D printing material waste through its recycling program.
“Our Mindful Manufacturing approach enables more sustainable production, for manufacturing applications across supply chains, optimizing overall environmental impacts. Being ESG and sustainability minded reduces risk and promotes the healthy management of our successful global enterprise.” commented Stratasys CEO Yoav Zeif.
“We are proud to spearhead this effort in our industry and with our customers, supporting decarbonization strategies across a wide array of product portfolios and operations.”
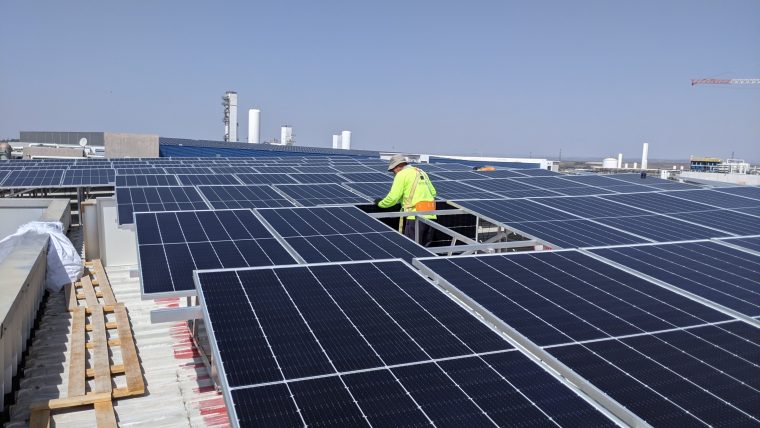

How sustainable is Stratasys?
Back in 2021, Stratasys officially committed to achieving circular economy processes, climate action, and social change with the 3D printing industry. At the time, it announced its intention to pursue a sustainability agenda based on the United Nations’ (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
As such, the company joined the Additive Manufacturer Green Trade Association (AMGTA) as a Founding Member. The AMGTA was created in 2019 by Sintavia, Taito Nippon Sanso Corporation and QC Laboratories, to promote the green credentials of 3D printing and advance industry sustainability.
Three years on, has Stratasys delivered on these claims? The new ESG report includes quantitative data covering 2021-2022 and qualitative information up until the end of 2023. During this period, the company reduced water intensity by 32.5% across its global operations, leading to a 6.8% reduction in water usage.
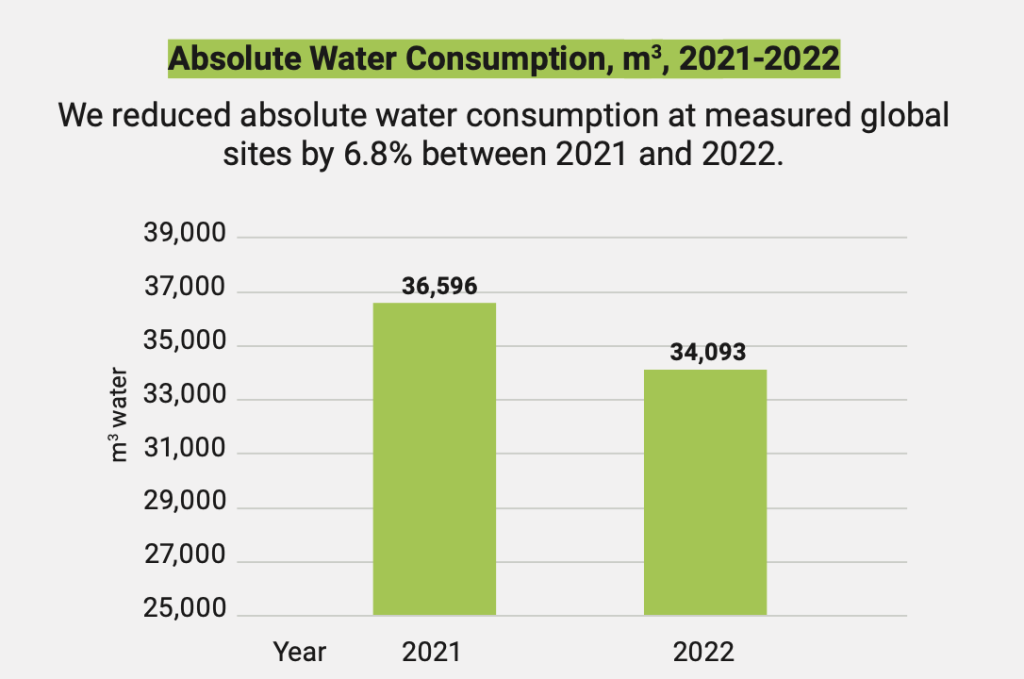
Stratasys also installed solar panels at its Israel facilities, generating 441,339 kWh of renewable energy. The 207 tons of CO2 savings equate to the impact of planting 3,423 trees. An 11.3% increase in the number of recycled filament spools, cartridges and canisters was also achieved through a recycling and returns program.
The new ESG report represents the first time Stratasys has disclosed data on waste management. The company claims that its European, American and Israeli facilities implement waste management initiatives to reduce contributions to landfills. In 2022, the company diverted 399 metric tons of waste from landfills across measured sites. This was achieved by its single-stream, cardboard and plastic recycling programs.
Stratasys also points to its role in the AMGTA’s Lifecycle Inventory Research Report, which highlighted the sustainability benefits of 3D printing in the fashion sector. This year-long study analyzed the cradle-to-gate environmental impact of a 3D logo attached to the heel of a luxury athletic shoe.
Stratasys’ Polyjet J850 TechStyle 3D printer enabled a 24.8% reduction in CO2e emissions, and a 48% reduction in stock material compared to a traditional multi-step 2D inkjet printing and thermal welding production process.
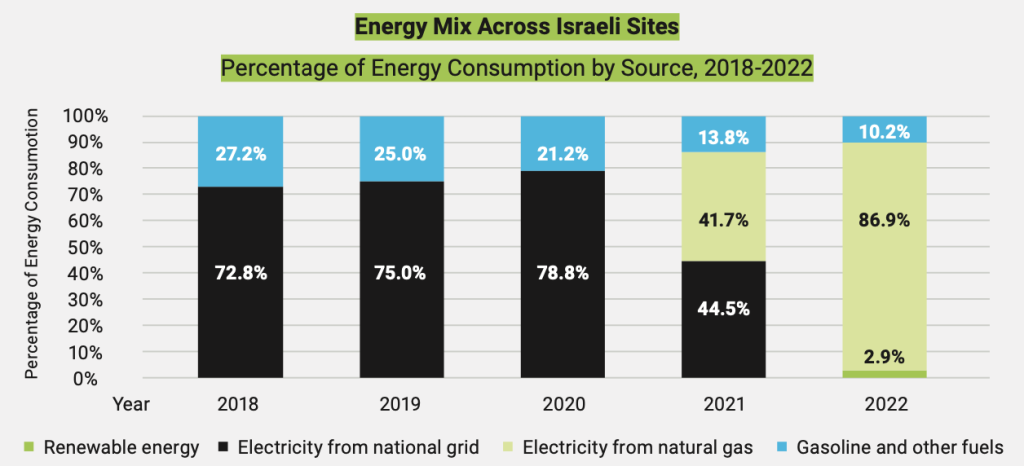
The 3D printer manufacturer has also received The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 14001 Environmental Management certification at its Israel-based headquarters for the second year running. This internationally recognized standard provides a framework for organizations to implement an environmental management system, and continually improve environmental performance.
To achieve this recognition, Stratasys was required to implement energy, waste and water tracking systems. A gap analysis was also completed, along with internal and external audits.
Stratasys highlights its social achievements
Away from sustainability, Stratasys has committed to delivering on key social and administration goals. According to the ESG report, more than 38,000 hours of employee training were provided, equating to 18 hours per employee. Additionally, 81% of managers participated in management training during the reviewed period.
Employee engagement is also said to be high, with a 78% participation rate in the last employee survey. Here, an all-time high engagement score of 73 was achieved.
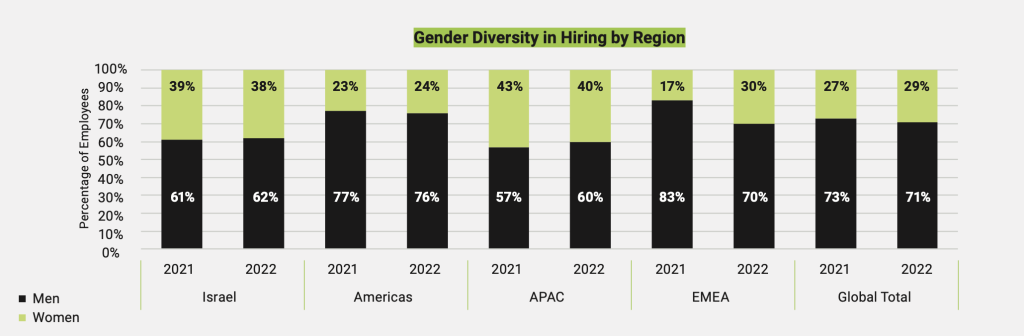
Stratasys has also highlighted diversity as being a key focus of its hiring practices. In 2022, the company set 4 diversity KPIs. For instance, 100% of candidate slates for management and above will have a diverse slate. 35% of management hires will be women, with a figure of 25% for tech positions. Additionally, the firm has committed to ensuring that 40% of intern/student hires will reflect ethnicity and gender diversity.
In terms of governance, all new suppliers in 2021 and 2022 signed the Supplier Code of Conduct. This includes environmental, social and ethical standards. What’s more, over 97% of Stratasys employees completed compliance training in anti-harassment, safety, and the firm’s Code of Ethics. Finally, no product-related health and safety incidents of noncompliance occurred between 2021-2022.
Sustainability in additive manufacturing
The 3D printing industry is currently witnessing a prominent focus on environmental sustainability. Indeed, this theme was heavily reflected within the responses of 3D printing experts in recent surveys on 3D printing trends and future of 3D printing.
Indeed, Stratasys is not the only 3D printing firm working to promote green manufacturing practices. Earlier this month, UK-based 3D printing filament manufacturer Filamentive launched a new free PLA 3D Printing waste recycling service.
The first scheme of its kind in the UK, the service is designed to combat pollution in FDM 3D printing. According to the company, 33% of 3D printed parts end up as waste in the UK. This translates to 400,000 kg of plastic.
Filamentive’s new service seeks to remove barriers to material recycling, allowing existing customers to return their 3D printing plastic waste for free. This is then recycled into new products, creating a sustainable UK-based circular supply chain.
Elsewhere, German 3D printer manufacturer EOS has developed a 3D printing cost and carbon calculator to encourage its customers to pursue sustainable manufacturing practices. This online tool provides a transparent analysis of the CO2 output of 3D printing compared to alternative manufacturing methods for any given metal parts.
According to EOS CEO Marie Langer, this makes it easy “for our customers looking at specific applications to calculate carbon emissions and also share the pricing to really evaluate the green business case.”
Danish AM Hub offers a similar tool, the CO2e calculator, which allows users to visualize the sustainability benefits of 3D printing compared to alternative manufacturing methods. The tool compares a traditional manufacturing process, such as milling, with 3D printing for a given component. It then outputs a single number, highlighting the amount CO2 saved or gained by using additive manufacturing.
What does the future of 3D printing hold?
What near-term 3D printing trends have been highlighted by industry experts?
Subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter to keep up to date with the latest 3D printing news.
You can also follow us on Twitter, like our Facebook page, and subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry Youtube channel to access more exclusive content.
Featured image shows rooftop solar panel installation at Stratasys’ Kiryat Gat manufacturing facility. Photo via Stratasys.

